Dispatcher Servlet
디스패처 서블릿의 dispatch는 "보내다" 라는 의미에 맞게 HTTP 프로토콜로 들어오는 모든 요청을 가장 먼저 받아 적합한 컨트롤러로 위임해주는 Front Controller입니다.
이를 조금 자세하게 설명하면, 클라이언트에서 어떤 요청이 오면 Tomcat과 같은 서블릿 컨테이너가 요청을 받게 됩니다. 그리고 이 모든 요청을 Dispatcher Servlet이 가장 먼저 받게 됩니다. 이후 Dispatcher Servlet은 공통적인 작업을 먼저 처리한 후 해당 요청을 처리해야 하는 컨트롤러를 찾아 작업을 위암하게 됩니다.
여기서 Front Controller라는 용어가 사용되는데, 이는 주로 서블릿 컨테이너의 제일 앞에서 서버로 들어오는 클라이언트의 모든 요청을 받아 처리해주는 컨트롤러로, MVC 구조에서 함꼐 사용되는 디자인 패턴입니다.
과거에는 모든 서블릿을 URL 매핑을 위해 web.xml에 등록해줘야 했지만, Dispatcher Servlet이 해당 어플리케이션으로 들어오는 모든 요청을 핸들링해주고, 공통 작업을 처리하면서 편리하게 이용할 수 있게 되었습니다.
결국 컨트롤러를 구현해두기만 하면 Dispatcher Servlet이 알아서 적합한 컨트롤러를 위임해주는 구조가 되었습니다.
실제 Dispatcher Servlet의 계층 구조는 다음과 같은 모습입니다.

위에서 우리가 주목해야할 부분은 다음과 같습니다.
- HttpServlet
- HttpServletBean
- FrameworkServlet
- DispatcherServlet
더 자세히 본다면 DispatcherServlet -> FrameworkServlet -> HttpServletBean -> HttpServlet -> Servlet 순으로 상속 관계가 형성되어 있습니다.
Servlet
서블릿은 웹 서버 내에서 실행되는 자바 프로그램으로, HTTP 통신을 사용하여 웹 클라이언트로부터 요청을 받고 응답하는 기술입니다. 일반적인 서블릿을 상속하는 GenericServlet과 HTTP 서블릿을 상속하는 HTTPServlet이 존재합니다.
GenericServlet
프로토콜에 독립적인 일반 서블릿입니다.
HttpServlet
웹 사이트에 적합한 HTTP 서블릿입니다. HttpServlet의 하위 클래슨느 아래 메서드 중 최소 하나의 메서드를 재정의해야 합니다.
doGet(),doPost(),doPut(),doDelete()init(),destroy()getServletInfo()
DispatcherServlet도 서블릿의 일종이므로, 소스코드를 타고 내려가다보면 위의 메서드를 재정의하고 있습니다.
HttpServletBean
HttpServlet의 확장 클래스로 스프링이 구현한 모든 서블렛 유형에 적합한 서블릿입니다.
FrameworkServlet
스프링 웹 프레임워크의 기본 서블릿입니다. 해당 클래스의 하위 클래스는 요청을 처리하기 위해 doService() 메서드를 정의해야 합니다.
public abstract class FrameworkServlet extends HttpServletBean implements ApplicationContextAware {
// 중략
protected abstract void doService(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception;
}
Dispatcher Servlet의 초기화 과정
Dispatcher Servlet은 HttpServlet 클래스의 상속을 통해 확장한 서블릿 기반의 기술이빈다. 따라서 Dispatcher Servlet 역시 일반적인 Servlet의 life cycle을 따르게 되는데 이는 다음과 같습니다.

init(): 요청이 들어오면 Servlet이 웹 컨테이너에 등록되어 있는지 확인하고, 없으면 초기화를 진행함service(): 요청이 들어오면 각각의 HTTP 메소드에 맞게 요청을 처리함destroy(): 서블릿이 종료되면 자원을 해제함
클라이언트로부터 요청이 오면 Servlet Container는 서블릿이 초기화 되었는지 확인하고, 초기화되지 않았다면 init() 메소드를 통해 호출을 초기화합니다. 해당 메서드는 첫 요청이 왔을 때 한번만 실행되므로 서블릿의 쓰레드에서 공통적으로 필요로 하는 작업들이 진행됩니다.
그 작업들 중에는 Dispatcher Servlet이 controller로 요청을 위임하고 받은 결과를 처리하기 위한 도구들을 준비하는 과정이 존재합니다. 그 도구들은 다음과 같습니다.
@Nullable
private MultipartResolver multipartResolver; // Multipart 파일 업로드를 위한 Resolver
@Nullable
private LocaleResolver localeResolver; // Locale 정보를 해석하기 위한 Resolver
@Nullable
private List<HandlerMapping> handlerMappings; // 요청을 처리할 Controller를 찾기 위한 Mapping
@Nullable
private List<HandlerAdapter> handlerAdapters; // 요청을 처리할 Controller를 실행하기 위한 Adapter
@Nullable
private List<HandlerExceptionResolver> handlerExceptionResolvers; // 예외 처리를 위한 Resolver
@Nullable
private RequestToViewNameTranslator viewNameTranslator; // View 이름을 찾기 위한 Translator
@Nullable
private List<ViewResolver> viewResolvers; // View를 찾기 위한 Resolver
@Nullable
private FlashMapManager flashMapManager; // FlashMap을 관리하기 위한 Manager
Spring은 Lazy-Init 전략을 사용하여 어플리케이션을 바르게 구동하고 있어, 첫 요청이 들어와 서블릿 초기화가 진행될 때 ApplicationContext로부터 해당 빈을 찾아 설정해줍니다. 그리고 이는 스프링의 첫 요청을 느리게 만드는 원인입니다.
실제 코드에서 들여다보면 다음과 같습니다.
protected void onRefresh(ApplicationContext context) {
this.initStrategies(context);
}
protected void initStrategies(ApplicationContext context) {
this.initMultipartResolver(context);
this.initLocaleResolver(context);
this.initThemeResolver(context);
this.initHAndlerMappings(context);
this.initHandlerAdapters(context);
this.initHandlerExceptionResolvers(context);
this.initRequestToViewNameTranslator(context);
this.initViewResolvers(context);
this.initFlashMapManager(context);
}
초기화해주는 메소드의 이름이 initStrategies인 이유는 전략 패턴이 적용되었기 때문입니다.
스프링은 유연하게 도구들을 사용할 수 있도록 전략 패턴을 사용하여 각 도구들을 초기화해주고 있습니다.
Dispatcher Servlet의 동작 과정
Dispatcher Servlet은 적합한 컨트롤러와 메소드를 찾아 요청을 위임해야 합니다. 다음과 같은 처리 과정이 존재합니다.
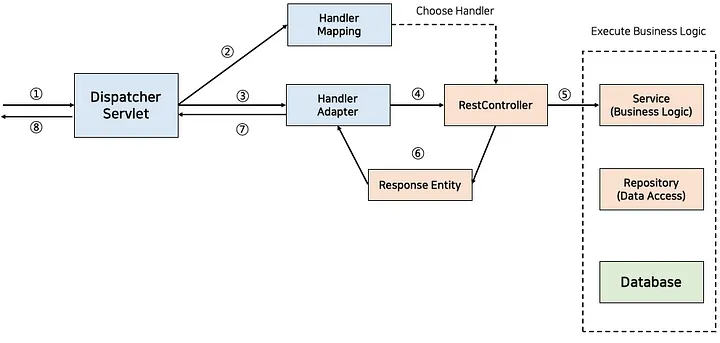
- 클라이언트로부터 요청이 들어오면 Dispatcher Servlet이 해당 요청을 가장 먼저 받게 됩니다.
- Dispatcher Servlet은 Handler Mapping을 통해 적합한 컨트롤러를 찾아내게 됩니다.
- 찾아낸 컨트롤러는 Handler Adapter를 통해 전달됩니다.
- Handler Adapter가 컨트롤러로 요청을 전달하게 됩니다.
- 컨트롤러의 메소드가 실행되면서 비즈니스 로직을 처리합니다.
- 컨트롤러는 처리한 결과를 Response Entity에 담아 Handler Adapter에 반환합니다.
- Handler Adapter는 Dispatcher Servlet에 결과를 반환합니다.
- Dispatcher Servlet은 View Resolver를 통해 해당 결과를 클라이언트에 반환합니다.
아래에서는 소스코드를 통해서 Dispatcher Servlet의 동작 과정을 살펴보겠습니다.
DispatcherServlet이 요청을 받아 처리하는 과정을 크게 살펴보면 다음과 같습니다.
- HttpServlet에서 Servlet 요청/응답 객체를 HttpServlet 요청/응답 객체로 변환
- FrameworkServlet에서 클라이언트의 요청을 HTTP Method에 따라 분기처리 (doXXX 메서드)
- DispatcherServlet에서 요청 정보에 대해 이를 처리할 Handler를 찾고, HandlerAdapter를 통해 Controller에 위임
3번 과정에서 요청에 매핑되는 HandlerMapping(HandlerExecutionChain)을 조회, Handler을 수행할 수 있는 HandlerAdapter 조회, HandlerAdapter를 통해 실제 Controller의 비즈니스 호출을 수행합니다.
우선 HttpServlet에서 Servlet 요청/응답 객체를 HttpServlet 요청/응답 객체로 변환하는 과정을 살펴보겠습니다.
public abstract class HttpServlet extends GenericServlet {
// 중략
public void service(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse res) throws ServletException, IOException {
HttpServletRequest request;
HttpServletResponse response;
try {
request = (HttpServletRequest)req;
response = (HttpServletResponse)res;
} catch (ClassCastException var6) {
throw new ServletException(lStrings.getString("http.non_http"));
}
this.service(request, response);
}
protected void service(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
String method = req.getMethod();
long lastModified;
if (method.equals("GET")) {
lastModified = this.getLastModified(req);
if (lastModified == -1L) {
this.doGet(req, resp);
} else {
long ifModifiedSince;
try {
ifModifiedSince = req.getDateHeader("If-Modified-Since");
} catch (IllegalArgumentException var9) {
ifModifiedSince = -1L;
}
if (ifModifiedSince < lastModified / 1000L * 1000L) {
this.maybeSetLastModified(resp, lastModified);
this.doGet(req, resp);
} else {
resp.setStatus(304);
}
}
} else if (method.equals("HEAD")) {
lastModified = this.getLastModified(req);
this.maybeSetLastModified(resp, lastModified);
this.doHead(req, resp);
} else if (method.equals("POST")) {
this.doPost(req, resp);
} else if (method.equals("PUT")) {
this.doPut(req, resp);
} else if (method.equals("DELETE")) {
this.doDelete(req, resp);
} else if (method.equals("OPTIONS")) {
this.doOptions(req, resp);
} else if (method.equals("TRACE")) {
this.doTrace(req, resp);
} else {
String errMsg = lStrings.getString("http.method_not_implemented");
Object[] errArgs = new Object[]{method};
errMsg = MessageFormat.format(errMsg, errArgs);
resp.sendError(501, errMsg);
}
}
// 중략
}
먼저 클라이언트의 요청은 DispatcherServlet의 부모 추상 클래스인 HttpServlet의 service() 메서드에서 요청을 받습니다. 위 코드에서 Servlet 객체인 경우 이를 HttpServlet 객체로 변환합니다.
아닌 경우는 매개변수에 따라 overloading된 service() 메서드를 호출하게 되는데, 이 메서드는 HTTP Method에 따라 doGet(), doPost() 등을 호출하게 됩니다.
Servlet 객체를 캐스팅하는 service() 메서드에서 마지막에 this.service(request, response)를 호출하게 되는데, 이는 FrameworkServlet 추상 클래스에서 재정의된 service() 메서드를 호출하게 됩니다.
public abstract class FrameworkServlet extends HttpServletBean implements ApplicationContextAware {
private static final Set<String> HTTP_SERVLET_METHODS = Set.of("DELETE", "HEAD", "GET", "OPTIONS", "POST", "PUT", "TRACE");
// 중략
protected void service(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
if (HTTP_SERVLET_METHODS.contains(request.getMethod())) {
super.service(request, response);
} else {
this.processRequest(request, response);
}
}
// 중략
}
FrameworkServlet에서 HTTP Method에 따라 분기처리가 진행되는데, HTTP Method가 Servlet Method에 포함되어 있으면 HttpServlet의 service() 메서드를 호출하게 됩니다.
그렇지 않은 경우, 예를 들면 PATCH, 등의 Method가 들어오면 processRequest() 메서드를 호출하게 됩니다.
doXXX 메서드에서 doPatch() 등의 메서드가 존재하지 않는데, 이유는 다음과 같습니다.
Servlet api 3.0을 정의한 JSR 315에서 patch 메서드에 대해 인식하지 못했기 때문에 doPatch() 메서드를 구현하지 못했고, 이후 PATCH 메서드가 HTTP 프로토콜에 추가되면서 Spring 패키지에 속하는 FrameworkServlet 클래스에서 분기 처리를 통해 Http Method가 PATCH인 케이스와 그 외의 케이스를 구분하여 처리하도록 대응했습니다.
그 외에 정의되어있는 HTTP Method에 대해서는 HttpServlet의 service() 메서드를 호출하게 됩니다. 해당 메서드는 위의 HttpServlet에서 overloading을 통해 HttpServlet 매개변수를 사용하는 service() 메서드입니다.
HttpServlet의 service() 메서드에서는 HTTP Method에 따라 doGet(), doPost() 등을 호출하게 되는데, 이는 DispatcherServlet에서 요청을 처리하기 위한 Handler를 찾고, HandlerAdapter를 통해 Controller에 위임하는 과정입니다.
public abstract class FrameworkServlet extends HttpServletBean implements ApplicationContextAware {
// 중략
protected final void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
this.processRequest(request, response);
}
protected final void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
this.processRequest(request, response);
}
protected final void doPut(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
this.processRequest(request, response);
}
protected final void doDelete(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
this.processRequest(request, response);
}
// 중략
}
실제 호출은 HttpServlet 클래스를 상속받고, doXXX 메서드를 오버라딩하고 있는 자식 클래스의 doXXX 메서드입니다. 즉, HttpServlet 추상 클래스에서 템플릿을 제공하고, 실제 비즈니스 로직은 이를 상속받는 FrameworkServlet에 구현되어 있는데, 이는 템플릿 메서드 패턴이 적용되어있음을 알 수 있습니다. 템플릿 메서드 패턴에 대해서 잘 모르신다면 여기를 참고해주세요.
자식 클래스에서 정의된 doXXX 메서드는 위와 같이 모두 processRequest() 메서드를 호출하도록 되어있습니다.
public abstract class FrameworkServlet extends HttpServletBean implements ApplicationContextAware {
// 중략
protected final void processRequest(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
Throwable failureCause = null;
LocaleContext previousLocaleContext = LocaleContextHolder.getLocaleContext();
LocaleContext localeContext = this.buildLocaleContext(request);
RequestAttributes previousAttributes = RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes();
ServletRequestAttributes requestAttributes = this.buildRequestAttributes(request, response, previousAttributes);
WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);
asyncManager.registerCallableInterceptor(FrameworkServlet.class.getName(), new RequestBindingInterceptor());
this.initContextHolders(request, localeContext, requestAttributes);
try {
this.doService(request, response);
} catch (IOException | ServletException var16) {
Exception ex = var16;
failureCause = ex;
throw ex;
} catch (Throwable var17) {
Throwable ex = var17;
failureCause = ex;
throw new ServletException("Request processing failed: " + ex, ex);
} finally {
this.resetContextHolders(request, previousLocaleContext, previousAttributes);
if (requestAttributes != null) {
requestAttributes.requestCompleted();
}
this.logResult(request, response, (Throwable)failureCause, asyncManager);
this.publishRequestHandledEvent(request, response, startTime, (Throwable)failureCause);
}
}
// 중략
}
해당 메서드에서의 핵심 로직은 try문 내에 존재하는 doService()입니다. 바로 이 메서드가 DispatcherServlet 클래스를 호출하는 진입점입니다.
public class DispatcherServlet extends FrameworkServlet {
// 중략
protected void doService(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
this.logRequest(request);
Map<String, Object> attributesSnapshot = null;
if (WebUtils.isIncludeRequest(request)) {
attributesSnapshot = new HashMap();
Enumeration<?> attrNames = request.getAttributeNames();
label116:
while(true) {
String attrName;
do {
if (!attrNames.hasMoreElements()) {
break label116;
}
attrName = (String)attrNames.nextElement();
} while(!this.cleanupAfterInclude && !attrName.startsWith("org.springframework.web.servlet"));
attributesSnapshot.put(attrName, request.getAttribute(attrName));
}
}
request.setAttribute(WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, this.getWebApplicationContext());
request.setAttribute(LOCALE_RESOLVER_ATTRIBUTE, this.localeResolver);
request.setAttribute(THEME_RESOLVER_ATTRIBUTE, this.themeResolver);
request.setAttribute(THEME_SOURCE_ATTRIBUTE, this.getThemeSource());
if (this.flashMapManager != null) {
FlashMap inputFlashMap = this.flashMapManager.retrieveAndUpdate(request, response);
if (inputFlashMap != null) {
request.setAttribute(INPUT_FLASH_MAP_ATTRIBUTE, Collections.unmodifiableMap(inputFlashMap));
}
request.setAttribute(OUTPUT_FLASH_MAP_ATTRIBUTE, new FlashMap());
request.setAttribute(FLASH_MAP_MANAGER_ATTRIBUTE, this.flashMapManager);
}
RequestPath previousRequestPath = null;
if (this.parseRequestPath) {
previousRequestPath = (RequestPath)request.getAttribute(ServletRequestPathUtils.PATH_ATTRIBUTE);
ServletRequestPathUtils.parseAndCache(request);
}
try {
this.doDispatch(request, response);
} finally {
if (!WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request).isConcurrentHandlingStarted() && attributesSnapshot != null) {
this.restoreAttributesAfterInclude(request, attributesSnapshot);
}
if (this.parseRequestPath) {
ServletRequestPathUtils.setParsedRequestPath(previousRequestPath, request);
}
}
}
// 중략
}
해당 메서드의 핵심 로직은 doDispatch() 메서드입니다. 이 함수에서 아래의 작업을 진행하게 됩니다.
- 요청에 매핑되는 HandlerMapping(HandlerExecution) 조회
- HandlerAdapter 조회
- HandlerAdapter를 통해 Controller에 위임
public class DispatcherServlet extends FrameworkSErvlet {
// 중략
protected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
HttpServletRequest processedRequest = request;
HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler = null;
boolean multipartRequestParsed = false;
WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);
try {
try {
ModelAndView mv = null;
Exception dispatchException = null;
try {
processedRequest = this.checkMultipart(request);
multipartRequestParsed = processedRequest != request;
// 요청에 매핑되는 HandlerMapping 조회
mappedHandler = this.getHandler(processedRequest);
if (mappedHandler == null) {
this.noHandlerFound(processedRequest, response);
return;
}
// Handler를 수행할 수 있는 HandlerAdapter 조회
HandlerAdapter ha = this.getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler());
String method = request.getMethod();
boolean isGet = HttpMethod.GET.matches(method);
if (isGet || HttpMethod.HEAD.matches(method)) {
long lastModified = ha.getLastModified(request, mappedHandler.getHandler());
if ((new ServletWebRequest(request, response)).checkNotModified(lastModified) && isGet) {
return;
}
}
// 등록된 Interceptor의 preHandle 수행 (컨트롤러 실행 전)
if (!mappedHandler.applyPreHandle(processedRequest, response)) {
return;
}
// HandlerAdapter를 통해 Controller 호출
mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler());
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
return;
}
this.applyDefaultViewName(processedRequest, mv);
// 등록된 Interceptor의 postHandle 수행 (컨트롤러 실행 후)
mappedHandler.applyPostHandle(processedRequest, response, mv);
} catch (Exception var20) {
Exception ex = var20;
dispatchException = ex;
} catch (Throwable var21) {
Throwable err = var21;
dispatchException = new ServletException("Handler dispatch failed: " + err, err);
}
// Dispatch 결괴 처리
this.processDispatchResult(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, mv, (Exception)dispatchException);
} catch (Exception var22) {
Exception ex = var22;
triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, ex);
} catch (Throwable var23) {
Throwable err = var23;
triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, new ServletException("Handler processing failed: " + err, err));
}
} finally {
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
if (mappedHandler != null) {
mappedHandler.applyAfterConcurrentHandlingStarted(processedRequest, response);
}
asyncManager.setMultipartRequestParsed(multipartRequestParsed);
} else if (multipartRequestParsed || asyncManager.isMultipartRequestParsed()) {
this.cleanupMultipart(processedRequest);
}
}
}
// 중략
}
다시 자세하게 살펴보자면
요청에 매핑되는 HandlerMapping(HandlerExecutionChain) 조회는 다음 메서드를 통해 이뤄집니다.
@Nullable
protected HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
if (this.handlerMappings != null) {
Iterator var2 = this.handlerMappings.iterator();
while(var2.hasNext()) {
HandlerMapping mapping = (HandlerMapping)var2.next();
HandlerExecutionChain handler = mapping.getHandler(request);
if (handler != null) {
return handler;
}
}
}
return null;
}
HandlerExecutionChain은 HandlerMethod, Interceptor들로 구성되어 HandlerMapping에 해당한느 클래스입니다.
HandlerExecutionChain
- Handler execution chain, consisting of handler object and any handler interceptors.
- Returned by HandlerMapping's HandlerMapping.getHandler method.
DispatcherServlet이 HandlerExecutionChain 객체를 얻는 이유는 doDispatch() 메서드에 등록된 인터셉터를 처리 하는 로직이 존재하기 때문입니다.(applyPreHandle, applyPostHandle)
mapping.getHandler(request)를 더 타고 들어가보겠습니다.
public abstract class AbstractHandlerMapping extends WebApplicationObjectSupport implements HandlerMapping, Ordered, BeanNameAware {
// 중략
@Nullable
public final HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
Object handler = this.getHandlerInternal(request);
if (handler == null) {
handler = this.getDefaultHandler();
}
if (handler == null) {
return null;
} else {
if (handler instanceof String) {
String handlerName = (String)handler;
handler = this.obtainApplicationContext().getBean(handlerName);
}
if (!ServletRequestPathUtils.hasCachedPath(request)) {
this.initLookupPath(request);
}
HandlerExecutionChain executionChain = this.getHandlerExecutionChain(handler, request);
if (request.getAttribute(SUPPRESS_LOGGING_ATTRIBUTE) == null) {
if (this.logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
this.logger.trace("Mapped to " + handler);
} else if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled() && !DispatcherType.ASYNC.equals(request.getDispatcherType())) {
this.logger.debug("Mapped to " + executionChain.getHandler());
}
}
if (this.hasCorsConfigurationSource(handler) || CorsUtils.isPreFlightRequest(request)) {
CorsConfiguration config = this.getCorsConfiguration(handler, request);
if (this.getCorsConfigurationSource() != null) {
CorsConfiguration globalConfig = this.getCorsConfigurationSource().getCorsConfiguration(request);
config = globalConfig != null ? globalConfig.combine(config) : config;
}
if (config != null) {
config.validateAllowCredentials();
config.validateAllowPrivateNetwork();
}
executionChain = this.getCorsHandlerExecutionChain(request, executionChain, config);
}
return executionChain;
}
}
@Nullable
protected abstract Object getHandlerInternal(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception;
// 중략
}
public abstract class RequestMappingInfoHandlerMapping extends AbstractHandlerMethodMapping<RequestMappingInfo> {
// 중략
@Nullable
protected HandlerMethod getHandlerInternal(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
request.removeAttribute(PRODUCIBLE_MEDIA_TYPES_ATTRIBUTE);
HandlerMethod var2;
try {
var2 = super.getHandlerInternal(request);
} finally {
ProducesRequestCondition.clearMediaTypesAttribute(request);
}
return var2;
}
// 중략
}
public abstract class AbstractHandlerMethodMapping<T> extends AbstractHandlerMapping implements InitializingBean {
// 중략
@Nullable
protected HandlerMethod getHandlerInternal(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
String lookupPath = this.initLookupPath(request);
this.mappingRegistry.acquireReadLock();
HandlerMethod var4;
try {
HandlerMethod handlerMethod = this.lookupHandlerMethod(lookupPath, request);
var4 = handlerMethod != null ? handlerMethod.createWithResolvedBean() : null;
} finally {
this.mappingRegistry.releaseReadLock();
}
return var4;
}
// 중략
}
해당 메서드를 타고 들어가보면 AbstractHandlerMethodMapping 추상 클래스의 getHandlerInternal() 메서드에서 HandlerMethod를 찾고, AbstractHandlerMapping 추상 클래스에서 HandlerExecutionChain 객체를 생성하여 리턴하는 것을 확인할 수 있다.
- lookupPath: URI
- mappingRegistry: HandlerMethod를 저장하는 맵
- handlerMethod: bean, beanFactory, Controller의 method 정보
이후 AbstractHandlerMapping 추상 클래스의 getHandler() 부분을 살펴보면 getHandlerInternal() 메서드를 수행한 후 handler의 타입은 HandlerMethod이고, 수행할 수 있는 인터셉터들을 포함하여 getHandlerExecutionChain() 메서드를 통해 HandlerExecutionChain 객체를 생성한다.
위 과정을 통해 HandlerMapping을 찾고, HandlerExecutionChain 객체를 생성하여 반환한다.
이후 HandlerAdapter를 찾기 위해 다음 메서드를 살펴보겠다. DispatcherServlet 클래스의 doDispatch() 메서드에서 getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler) 부분을 살펴보자.
만약 @GetMapping을 사용한 Controller에서 요청이 들어왔다고 가정하면, @GetMapping 어노테이션 내부에 RequestMapping() 어노테이션이 존재하기 때문에, getHandlerAdapter 메서드에서는 RequestMappingHandlerAdapter를 반환한다.
또한 위의 Handler는 HandlerMethod로 매핑되는 컨트롤러의 메서드 및 빈, 빈 팩토리 등이 저장되어 있다.
이제 HandlerAdapter를 통해 실제 Controller의 비즈니스 로직을 호출하는 곳을 가보겠다.
마찬가지로 DispatcherServlet 클래스의 doDispatch() 메서드에서 ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler()) 부분을 살펴보자. 해당 handle() 메서드를 타고 들어가다 보면 다음을 확인할 수 있다.
public abstract class AbstractHandlerMethodAdapter extends WebContentGenerator implements HandlerAdapter, Ordered {
// 중략
@Nullable
public final ModelAndView handle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception {
return this.handleInternal(request, response, (HandlerMethod)handler);
}
@Nullable
protected abstract ModelAndView handleInternal(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, HandlerMethod handlerMethod) throws Exception;
public final long getLastModified(HttpServletRequest request, Object handler) {
return this.getLastModifiedInternal(request, (HandlerMethod)handler);
}
// 중략
}
public class RequestMappingHandlerAdapter extends AbstractHandlerMethodAdapter implements BeanFactoryAware, InitializingBean {
// 중략
@Nullable
protected ModelAndView handleInternal(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, HandlerMethod handlerMethod) throws Exception {
this.checkRequest(request);
ModelAndView mav;
if (this.synchronizeOnSession) {
HttpSession session = request.getSession(false);
if (session != null) {
Object mutex = WebUtils.getSessionMutex(session);
synchronized(mutex) {
mav = this.invokeHandlerMethod(request, response, handlerMethod);
}
} else {
mav = this.invokeHandlerMethod(request, response, handlerMethod);
}
} else {
mav = this.invokeHandlerMethod(request, response, handlerMethod);
}
if (!response.containsHeader("Cache-Control")) {
if (this.getSessionAttributesHandler(handlerMethod).hasSessionAttributes()) {
this.applyCacheSeconds(response, this.cacheSecondsForSessionAttributeHandlers);
} else {
this.prepareResponse(response);
}
}
return mav;
}
// 중략
}
뭔가 운영체제에서 배웠던 무언가가 보이는데 이는 다음 기회에 살펴보는 것으로 하고, 확인해야 할 부분은 RequestMappingHandlerAdapter 클래스의 handlerInternal() 메서드에서 Controller를 호출하는 로직인 invokeHandlerMethod()메서드이다.
해당 메서드를 타고 들어가보면 다음과 같은 로직을 확인할 수 있다.
public class RequestMappingHandlerAdapter extends AbstractHandlerMethodAdapter {
// 중략
@Nullable
protected ModelAndView invokeHandlerMethod(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, HandlerMethod handlerMethod) throws Exception {
WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);
AsyncWebRequest asyncWebRequest = WebAsyncUtils.createAsyncWebRequest(request, response);
asyncWebRequest.setTimeout(this.asyncRequestTimeout);
asyncManager.setTaskExecutor(this.taskExecutor);
asyncManager.setAsyncWebRequest(asyncWebRequest);
asyncManager.registerCallableInterceptors(this.callableInterceptors);
asyncManager.registerDeferredResultInterceptors(this.deferredResultInterceptors);
response = (HttpServletResponse)asyncWebRequest.getNativeResponse(HttpServletResponse.class);
ServletWebRequest webRequest = asyncWebRequest instanceof ServletWebRequest ? (ServletWebRequest)asyncWebRequest : new ServletWebRequest(request, response);
WebDataBinderFactory binderFactory = this.getDataBinderFactory(handlerMethod);
ModelFactory modelFactory = this.getModelFactory(handlerMethod, binderFactory);
ServletInvocableHandlerMethod invocableMethod = this.createInvocableHandlerMethod(handlerMethod);
if (this.argumentResolvers != null) {
invocableMethod.setHandlerMethodArgumentResolvers(this.argumentResolvers);
}
if (this.returnValueHandlers != null) {
invocableMethod.setHandlerMethodReturnValueHandlers(this.returnValueHandlers);
}
invocableMethod.setDataBinderFactory(binderFactory);
invocableMethod.setParameterNameDiscoverer(this.parameterNameDiscoverer);
invocableMethod.setMethodValidator(this.methodValidator);
ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer = new ModelAndViewContainer();
mavContainer.addAllAttributes(RequestContextUtils.getInputFlashMap(request));
modelFactory.initModel(webRequest, mavContainer, invocableMethod);
mavContainer.setIgnoreDefaultModelOnRedirect(this.ignoreDefaultModelOnRedirect);
if (asyncManager.hasConcurrentResult()) {
Object result = asyncManager.getConcurrentResult();
Object[] resultContext = asyncManager.getConcurrentResultContext();
Assert.state(resultContext != null && resultContext.length > 0, "Missing result context");
mavContainer = (ModelAndViewContainer)resultContext[0];
asyncManager.clearConcurrentResult();
LogFormatUtils.traceDebug(this.logger, (traceOn) -> {
String formatted = LogFormatUtils.formatValue(result, !traceOn);
return "Resume with async result [" + formatted + "]";
});
invocableMethod = invocableMethod.wrapConcurrentResult(result);
}
// 실제 Controller 호출
invocableMethod.invokeAndHandle(webRequest, mavContainer, new Object[0]);
return asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted() ? null : this.getModelAndView(mavContainer, modelFactory, webRequest);
}
// 중략
}
해당 메서드에서는 ServletInvocableHandlerMethod invocableMethod = createInvocableHandlerMethod(...)를 통해 ServletInvocableHandlerMethod 객체를 생성하고 있다.
그렇다면 ServletInvocableHandlerMethod 객체는 무엇일까? 이는 HandlerMethod를 상속받고 있는 클래스 중 하나이다. 이는 등록된 HandlerMethodReturnValueHandler를 통해 반환 값을 처리하는 기능으로 InvocableHandlerMethod를 상속받고, 메서드 레벨에서의 @ResponseStatus 어노테이션을 통해 응답 상태를 설정할 수 있다.
그리고 InvocableHandlerMethod는 HandlerMethodArgumentResolver 리스트를 통해 현재 HTTP 요청에서 받은 인수 값으로 기본 메서드를 호출하는 HandlerMethod를 상속받는 클래스이다. 즉, ServletInvocableHandlerMethod는 HandlerMethod와 함께 컨트롤러의 파라미터 및 반환값을 처리하기 위한 객체임을 유추할 수 있다.
결국 createInvocableHandlerMethod()메서드를 통해 ServletInvocableHandlerMethod 객체를 생성하고, 이때, bean, beanFactory, method, parameters 등의 변수가 초기화되어 생성된다.
이렇게 객체의 생성 및 설정이 끝나면 invokeAndHandle() 메서드가 실행된다. 해당 메서드는 Controller의 메서드를 실행하고 반환 값을 처리하는 메서드이다. 여기에서 반환 값에 따라 ModelAndView, ResponseEntity, ResponseBody 등을 각 Handler가 처리한다.
실제 처리는 부모 클래스인 InvocableHandlerMethod의 invokeForRequest() 메서드에서 이뤄진다.
public class InvocableHandlerMethod extends HandlerMethod {
// 중략
@Nullable
public Object invokeForRequest(NativeWebRequest request, @Nullable ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer, Object... providedArgs) throws Exception {
// Controller를 호출하기 위해 필요한 인자값 처리
Object[] args = this.getMethodArgumentValues(request, mavContainer, providedArgs);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Arguments: " + Arrays.toString(args));
}
if (this.shouldValidateArguments() && this.methodValidator != null) {
this.methodValidator.applyArgumentValidation(this.getBean(), this.getBridgedMethod(), this.getMethodParameters(), args, this.validationGroups);
}
Object returnValue = this.doInvoke(args);
if (this.shouldValidateReturnValue() && this.methodValidator != null) {
this.methodValidator.applyReturnValueValidation(this.getBean(), this.getBridgedMethod(), this.getReturnType(), returnValue, this.validationGroups);
}
return returnValue;
}
protected Object[] getMethodArgumentValues(NativeWebRequest request, @Nullable ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer, Object... providedArgs) throws Exception {
MethodParameter[] parameters = this.getMethodParameters();
if (ObjectUtils.isEmpty(parameters)) {
return EMPTY_ARGS;
} else {
Object[] args = new Object[parameters.length];
for(int i = 0; i < parameters.length; ++i) {
MethodParameter parameter = parameters[i];
parameter.initParameterNameDiscovery(this.parameterNameDiscoverer);
args[i] = findProvidedArgument(parameter, providedArgs);
if (args[i] == null) {
if (!this.resolvers.supportsParameter(parameter)) {
throw new IllegalStateException(formatArgumentError(parameter, "No suitable resolver"));
}
try {
// 실제 Argument 값을 처리
args[i] = this.resolvers.resolveArgument(parameter, mavContainer, request, this.dataBinderFactory);
} catch (Exception var10) {
Exception ex = var10;
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
String exMsg = ex.getMessage();
if (exMsg != null && !exMsg.contains(parameter.getExecutable().toGenericString())) {
logger.debug(formatArgumentError(parameter, exMsg));
}
}
throw ex;
}
}
}
return args;
}
}
@Nullable
protected Object doInvoke(Object... args) throws Exception {
// 요청을 처리할 Method 객체 (Java Reflection)
Method method = this.getBridgedMethod();
try {
if (KotlinDetector.isKotlinReflectPresent()) {
if (KotlinDetector.isSuspendingFunction(method)) {
return this.invokeSuspendingFunction(method, this.getBean(), args);
}
if (KotlinDetector.isKotlinType(method.getDeclaringClass())) {
return InvocableHandlerMethod.KotlinDelegate.invokeFunction(method, this.getBean(), args);
}
}
return method.invoke(this.getBean(), args);
} catch (IllegalArgumentException var8) {
IllegalArgumentException ex = var8;
this.assertTargetBean(method, this.getBean(), args);
String text = ex.getMessage() != null && !(ex.getCause() instanceof NullPointerException) ? ex.getMessage() : "Illegal argument";
throw new IllegalStateException(this.formatInvokeError(text, args), ex);
} catch (InvocationTargetException var9) {
InvocationTargetException ex = var9;
Throwable targetException = ex.getCause();
if (targetException instanceof RuntimeException runtimeException) {
throw runtimeException;
} else if (targetException instanceof Error error) {
throw error;
} else if (targetException instanceof Exception exception) {
throw exception;
} else {
throw new IllegalStateException(this.formatInvokeError("Invocation failure", args), targetException);
}
}
}
// 중략
}
invokeForRequest() 메서드에서는 getMethodArgumentValues() 메서드를 통해 Controller의 메서드를 호출하기 위한 인자값들을 처리한다. 보통 우리가 인자값을 처리하기 위해 사용하는 @RequestParam, @PathVariable 등의 어노테이션이 스프링의 ArgumentResolver를 통해 처리되고, 이와 관련된 작업이 수행되는 곳이 getMethodArgumentValues() 메서드이다.
인자값을 처리하고 나면 InvocableHandlerMethod로 돌아와 doInvoke() 메서드를 호출한다. 요청을 처리하면 이후 응답에 대한 처리를 하기 위해 ServletInvocableHandlerMethod에서 HandlerMethodReturnValueHandlerComposite를 사용하여 후처리하게 된다. 이는 List에 등록되어 있는 Handler 중에 위임하여 메서드 반환값을 처리하는 컴포지트 패턴을 적용하고 있다. 컴포지트 패턴에 대해서 잘 모르신다면 여기를 참고해주세요.
HandlerAdapter가 Controller에게 요청이 끝나면 다음에는 응답에 대한 후처리로 returnValueHandlers를 통해 처리된다. 이때, 로직에서 처리한 return type을 처리하게 된다. 보통 ResponseEntity가 반환값인 경우 HttpEntityMethodProcessor을 Handler로 사용한다.
또한 보통 @RestController어노테이션을 사용하는 경우 ModelAndView 대신 원하는 반환값을 반환하게 된다.
RequestResponseBodyMethodProcessor 내부에서는 input, output message를 생성하여 AbstractMessageConverterMethodProcessor 추상 클래스의 writeWithMessageConverters() 메서드를 호출하고, MediaType을 검사하여 적절한 HttpMessageConverter를 찾아 응답을 처리하고 결과를 반환한다.
[참고]

